A blood glucose test, often called a blood sugar test, is used by diabetics to check the levels of glucose in the blood, particularly at certain times of the day, such as after meals. The test involves analyzing a small pin-prick sample of blood using a blood sugar measurement device. The oral glucose tolerance test is used to test for the presence of diabetes.
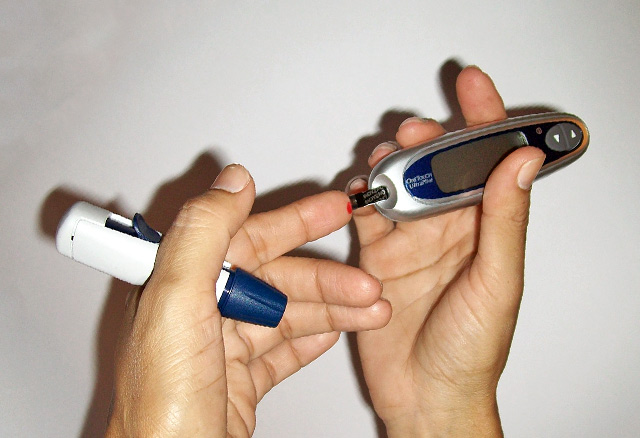 testing glucose level in a blood sample
testing glucose level in a blood sample equipment required: lancet, blood glucose strips, blood glucose analyzer, tissues.
procedure: Take a small blood sample from your fingertip, place it on a disposable test strip. Insert into the blood glucose analyzer and wait for the results. The machine may save the results, or you may have a diary to record the glucose level.
timing: the timing of the blood sample may depend on the aim of the test and the current treatment regime. Tests are often conducted a few times a day, such as a fasting measure before breakfast, before lunch/dinner, two hours after a meal, before bed, before exercise and if feeling unwell.
results: Blood glucose levels are measured in millimoles per liter of blood (mmol/L). Normal blood glucose levels are between 4.0–7.8mmol/L. The target range for diabetics will depend on the individual and the individual’s circumstances. The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep blood glucose levels within a specified target range, generally between 4 to 6 mmol/L (fasting). The test results can be used to help in the long-term management of diabetes.
notes: medications and taking regular blood tests is only one part of managing diabetes. It is also important to eat a healthy diet, maintain a healthy weight and perform regular exercise.
Related Pages
- Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) procedure
- Blood testing
- Other Health-Related Tests
- Article: Are you at Risk of Contracting Diabetes?
- Article: How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
- GI and Athletes — both high and low GI foods have a place in the diet of athletes.
- About diabetes
- Health Tests for Athletes


 Current Events
Current Events