Measuring the body's resting metabolism (how much energy the body is consuming at rest) can be useful for planning weight loss programs. One way to measure this is by direct calorimetry, using a box calorimeter to measure directly the heat produced by the body.
Human Whole Body Direct Calorimetry obtains a direct measurement of the energy use of the body by measuring the amount of heat generated by the body. To do this, the body is fully enclosed in a structure. The heat generated by body changes the temperature of the space, which is then measured, usually by changes in the temperature of water flowing through the walls.
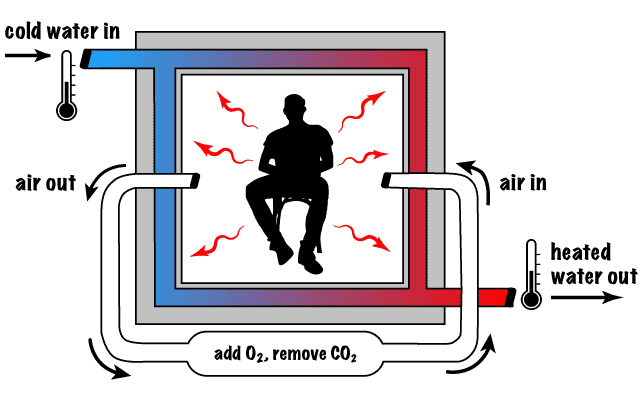 direct calorimetry set-up
direct calorimetry set-up This method is most commonly used in a resting situation, though it is still possible to use a calorimeter to measure the energy production during exercise. An easier and more reliable method of assessing energy consumption during exercise is indirect calorimetry. With this method, it is also possible to determine the respiratory exchange ratio to estimate the contribution of fats and carbohydrates for energy production.
Related Pages
- Method for measuring basal or resting metabolic rate using indirect calorimetry.
- Direct Calorimetry use during exercise
- All about Basal Metabolic Rate
- The calculations for indirect calorimetry measurement.
- All about the respiratory exchange ratio
- Equations for calculating BMR and RMR
- Power output and energy expenditure for running and walking
- About Energy Expenditure — methods, formula and calculators.
- Calories Burned Running — determines how many calories you have burned based on your weight and distance run.
- Daily Calorie Counter — determines how many calories you need each day
- Calculating Daily Energy Expenditure — a few formulas to estimate your daily energy expenditure.
- Lose weight while doing nothing — Not really nothing, but indirectly by changing your metabolism through exercise.


 Current Events
Current Events